Does Gum Recession Grow Back?
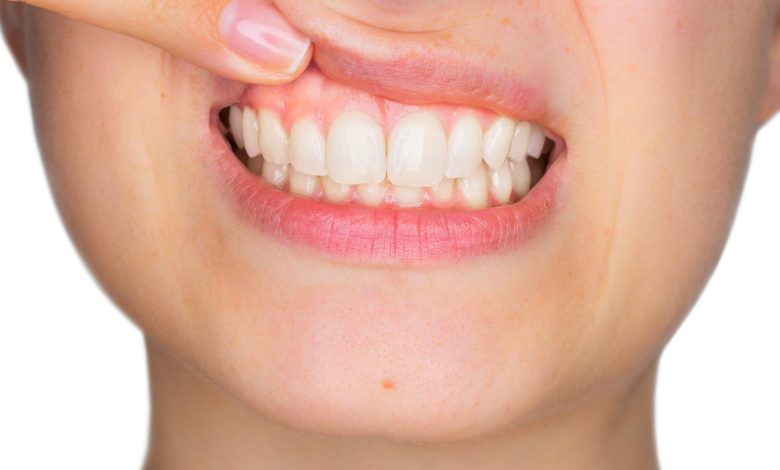
Many adults suffer from gum recession, where the gums pull away from the teeth and reveal more of the tooth. Some people think that once this recession happens, it will grow back to its original position, but that’s not always the case. In fact, what actually happens to gum recession after you stop brushing and flossing? Here’s what your dentist wants you to know about receding gums and what you can do to prevent them from getting worse.
Are there any treatments for gum recession?
Learn more about both here! Otherwise, it’s all about treating symptoms as they appear and educating yourself on how to keep things from getting worse in the future. One of our favorite methods for reducing inflammation in areas with gums recession is chewing sugar-free Trident gum!
How do I treat my receding gums?:
What happens when I stop flossing and brushing my teeth so well?
If you’re worried about gums recession, it’s easy to over-brush and over-floss. This is how your gums get even more irritated, which leads to more recession. The best solution for long-term gum health is frequent flossing and brushing, which removes bacteria but not so much that it irritates your gums. By going at a steady pace (just fast enough to hit every tooth), you can keep inflammation under control while reducing receding gums without risking tooth decay or gum disease. And when your dental routine feels too long and involved, remember: An ounce of prevention really is worth a pound of cure!
How do I know if I have gum recession or gingivitis?
If you’re unsure whether or not you have gum recession, you can check by placing a clean finger between your teeth and gums. If you feel indentations behind your teeth, it’s likely that your gums are receding. In addition to checking in-between your teeth, examine them as well to ensure there aren’t any holes or other damaged areas. If there are deep pockets in your gums, it could be an indication of gums recession and/or advanced periodontal disease (gum disease).
It’s important to understand that while recovery from gums recession is possible, it may not necessarily happen through conservative methods; healing may require invasive procedures such as dental grafting.
How does my dentist determine whether I have gum recession or something else?
Your dentist can tell whether you have gum recession or something else by inspecting your gums. If they see gingival recession at a distance of 2mm (approximately 1/10th of an inch) or more, you may want to
The real cause of your gum recession isn’t important, but knowing it is so that you can prevent it from happening again in future visits. Your dentist should be able to advise you on a few simple things that you can do to prevent further damage from occurring. For example, avoiding certain activities or foods might keep gum recession from occurring in future visits. If my dentist doesn’t know what’s causing my gum recession, can he/she still treat me?: Yes! Some causes of gum recession are easier to treat than others, depending on how advanced your condition is.
If I have gum recession, will it heal on its own with better dental care habits?
While gum recession can be helped with proper oral hygiene, it’s not reversible. While gum recession can be helped with proper oral hygiene, it’s not reversible. gum recession could become worse than when you first noticed it (or even lead to other oral health issues). The best way to prevent gum recession is by practicing excellent dental hygiene. Brush at least twice a day and remember to floss at least once; these practices will keep plaque from building up under your gums and slowly pulling them away from your teeth.
Are there any natural remedies that help with gums recession or other oral health concerns like bad breath or tooth sensitivity?
If you’re trying to cure gums recession, there are several natural remedies you can use to combat its effects. Start by brushing your teeth and gums regularly with a toothbrush that has soft bristles. Flossing will also help make sure that food particles don’t get stuck in areas between your teeth.
What are possible side effects of treatment for gum recession (dental implants, grafting, etc.)?
While there are some possible side effects of treatment for gum recession, they are usually mild and easily manageable. Most people do not experience serious complications or any complications at all. The most common complication that affects people receiving treatment for gum recession is a numbness of their tongue and lips. This side effect can be treated with medication or surgery if it becomes too bothersome. Another possible side effect is a lack of sensation around your mouth (the sides, lips, and tongue).
Should You Be Worried About Gum Recession?
If you’ve ever heard of gum recession, you may be wondering what it means and whether or not it affects your dental health. Gums recession occurs when the gum tissue recedes from the tooth, exposing it to plaque and other dental problems. While some gum recession can be prevented with routine brushing and flossing, other causes of gum recession include certain oral habits such as biting your fingernails or grinding your teeth while you sleep.
Are your gums receding?
The last thing you want is for your gums to recede, causing more teeth to become visible in your smile. Fortunately, gums recession doesn’t always lead to more tooth loss and there are things you can do about it. Here’s how to prevent and treat gum recession if you’re worried that it might happen to you: Brush and floss regularly: The main cause of gum recession is lack of oral hygiene. So, you have to brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush (ideally an electric one) and use dental floss at least once every day too. Visit your dentist regularly: As we said earlier, the main cause of gum recession is poor dental hygiene so see your dentist twice a year or so.
How does gum recession affect teeth?
If you’re worried about gum recession, you may also be curious about how it affects your teeth. To begin with, it’s worth noting that gums recession is most common in people who have genetic predispositions or risk factors. Certain oral health conditions can also make gum recession more likely. And, of course, there are lifestyle and personal choices that influence your risk too. If you smoke or drink heavily—or if you have a history of tooth-grinding—you could be putting yourself at greater risk for gums recession than someone who doesn’t do those things. As far as tooth-related risks go, orthodontic treatment and severe trauma can also put patients at greater risk for developing gums recession later on.
The causes of gums recession
A healthy set of teeth and gums requires daily brushing with a fluoride toothpaste, regular flossing, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and avoiding habits like smoking. Good oral hygiene is paramount to maintaining gum health. When you brush your teeth, don’t forget to scrape away any plaque buildup around your gums and under your gumline. If left to fester for too long, plaque can cause inflammation of soft tissue, which leads to recession. Another possible cause is clenching or grinding your teeth (bruxism). Using teeth-whitening products—including strips, trays or pens—also leads to gum recessions because they erode tooth enamel over time.
Gums recession treatment
It’s important to note that gums recession is not a sign of tooth decay. It doesn’t signal that you should be panicking over cavities, though it can certainly aggravate those existing in your mouth. If you find yourself experiencing gums recession, you might feel as if your teeth are being pushed back into your gums; they may even feel like they’re floating. The good news is that gums recession isn’t life-threatening and can almost always be fixed with treatment. To prevent future episodes of gums recession, avoid habits like clenching or grinding your teeth—or popping bubble wrap.
What should you do if you have gums recession?
If you have gums recession, there are some steps you can take to help protect your teeth. The most important thing is to brush and floss regularly (or using an electric toothbrush). For people with receding gums, use a soft-bristled toothbrush so as not to irritate sensitive tissues further. Brushing before bed is also recommended because that’s when plaque has more time to accumulate. This plaque can harden into tartar overnight, which makes it harder for your brush or floss to remove in one pass.
Prevention is key – it’s never too late to take action.
If you already have gums recession, there are steps you can take to slow down or prevent further receding. If you’re in your 40s or older, ask your dentist about recession-proofing your gums. Retaining as much gum tissue as possible—particularly around teeth prone to recession—can make a world of difference later on. Once gums recession has occurred and teeth have started to shift forward (even slightly), root planning may be able to prevent them from getting worse. The earlier treatment is initiated, however, the better!
| gum recession |